JavaScript try…catch Statement; In this tutorial, you will learn everything about JavaScript try...catch statement.
Sometimes, you are developing any web or app using javascript or any frameworks of javascript. That time no matter how much you experience in programming languages.
Because while developing the web and the app, some error remains. Usually, at that time script execution halt., If you will use try...catch statement in your js script, so this will help you to print errors to console.
JavaScript try...catch statement
The try…catch statement is used to handle errors in the js script.
The following syntax represents the try...catch statement:
try {
// code may cause error
} catch(error){
// code to handle error
}
Here,
- First, the code in
try {...}is executed. - If not come to errors in the script, then
catch(err)is ignored: the execution arrives at the finish oftryand goes on, skippingcatch. - If an error occurs,
tryexecution is stopped and jumps to thecatchblock. - If you want to see what error happened, you can access an
errorobject and display errors inside acatchblock.
So far, you have seen the above given syntax of try...catch and what it works.
But now you will learn by try...catch example and also will see the flowchart of try-catch, how work it.
The following flowchart represents the flow of the try...catch statement:
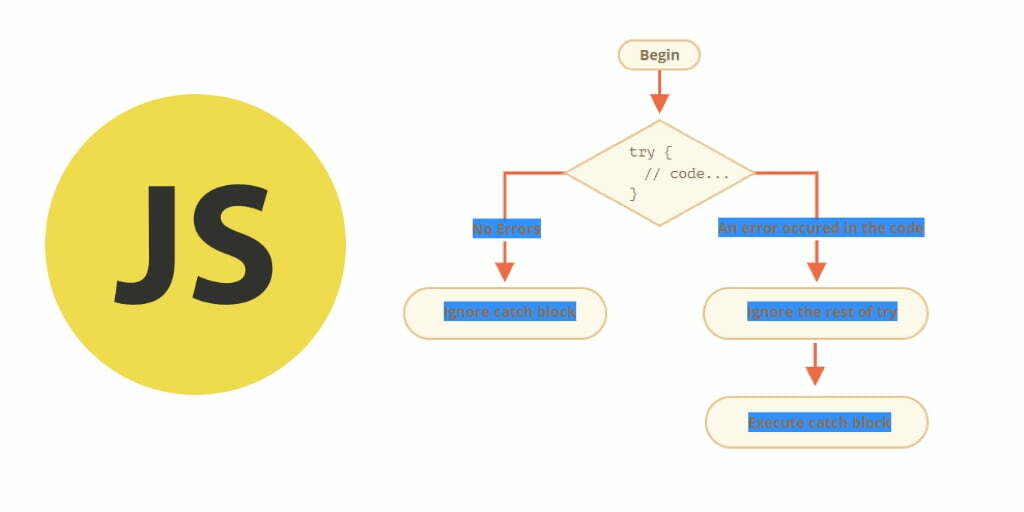
Let’s take a look an example of try...catch statement.
See the following example:
try {
myFunction();
} catch(error){
console.log(error); // print error object
}
Output
ReferenceError: myFunction is not defined
When you run the above example script, it display error myFunction() function doesn’t exist, therefore, JavaScript throws an error.
In javascript, the error object has two main properties:
- Error name
- Error message
If you are using a try..catch statement. And you want to print the custom in your script and program. So for this you have to use try/throw/catch statements.
Let’s take a look example using try/throw/catch statements:
try{
throw new Error ('This is a new error')
}
catch(error){
console.log(error)
console.log("End of try-catch block")
}
Output
Error: This is a new error
This example shows how you can create our own error in the throw block. Then try the code which should throw an error which should be caught by the catch block.
try…catch…finally statement
The try..catch statement has one more clause finally. This is a optional clause and it runs in all situations.
In other words, The piece of code always executes, which is written inside finally block.
The following syntax represents the try…catch…finally statement:
try {
... try to execute the code ...
} catch(e) {
... handle errors ...
} finally {
... execute always ...
}
Let’s take a look the following example:
function myFunc(){
try {
return 'try';
} catch(error) {
return 'catch';
} finally {
return 'finally';
}
}
console.log(myFunc());
Output
finally
Run the above script, it will return “finally” as output. Because no error happens in the try block. However, the try block to be ignored.
Note that two important points, if you are using try…catch…finally statement:
- If you remove the
finallyclause, themyFunction()function will return ‘first’ as output. - Once you use the
finallyclause, thecatchclause becomes optional.
Note that, The try..catch statement works to handle errors in a js script.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, you have learned everything about JavaScript try...catch statement as well as finally statement and using this how to handle errors in javascript